Chapter 1: Entrepreneurship
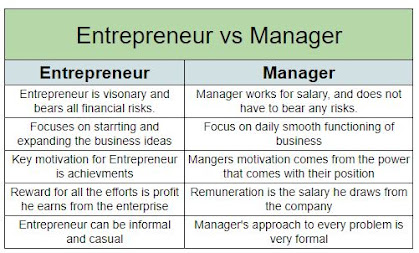
An entrepreneur is an individual who identifies and creates a new business venture or opportunity, assumes the associated risks, and takes responsibility for the outcomes. Entrepreneurs are often seen as innovators who disrupt traditional ways of doing things and create new products, services, or business models.
Intrapreneur: An intrapreneur is an employee of an organization who is given the freedom and resources to innovate, develop new ideas, and take risks within the context of their role in the organization. Intrapreneurs may develop new products, services, or business models that help the organization grow and adapt to changing market conditions.
Entrepreneurship: Entrepreneurship refers to the process of identifying a business opportunity, developing a new product or service, assembling the necessary resources, and launching a new venture. Entrepreneurs are individuals who take on the risks associated with starting a new business and are responsible for its success or failure.
Manager: A manager is an individual who is responsible for overseeing the operations of an organization or department. Managers are typically focused on ensuring that the organization achieves its goals and objectives by coordinating resources, delegating tasks, and making decisions about resource allocation.
Entrepreneur vs. Intrapreneur: While both entrepreneurs and intrapreneurs are involved in developing new ideas and taking risks, the key difference is that entrepreneurs are typically starting their own business or venture, while intrapreneurs are working within an existing organization.
Entrepreneur vs. Entrepreneurship: While the terms entrepreneur and entrepreneurship are often used interchangeably, there is a subtle difference between the two. Entrepreneurship refers to the process of identifying and pursuing a new business opportunity, while an entrepreneur is an individual who takes on the risks associated with starting and running a new venture.
Attributes and Characteristics of Successful Entrepreneurs:
- Visionary thinking
- Risk-taking propensity
- Passion and perseverance
- Creativity and innovation
- Resourcefulness and adaptability
- Decisiveness and action-orientation
- Strong work ethic and self-discipline
- Ability to learn from failure and setbacks
- Strong networking skills and ability to build relationships
- Customer-focused mindset
Functions of an Entrepreneur:
- Innovation and creativity
- Risk-taking and uncertainty management
- Resource mobilization and allocation
- Opportunity identification and exploitation
- Marketing and sales
- Financial management and planning
- Human resource management and leadership
- Networking and relationship building
Classification of Entrepreneurs:
- Small business entrepreneurs
- Scalable start-up entrepreneurs
- Social entrepreneurs
- Lifestyle entrepreneurs
- Corporate entrepreneurs
Role of Entrepreneur in Indian Economy
- Job creation and employment generation
- Economic growth and development
- Innovation and technological progress
- International competitiveness and trade
- Regional development and balanced growth
- Women and minority empowerment
- Rural and agricultural development
Developing Entrepreneurial Culture:
- Education and training
- Government policies and initiatives
- Access to capital and financing
- Business incubation and support services
- Mentoring and networking
- Promotion of innovation and technology
- Recognition and reward for entrepreneurship
- Cultural and societal attitudes towards entrepreneurship
Factors Influencing Entrepreneurship Growth:
- Economic factors (e.g. GDP growth, interest rates, inflation, tax policies, access to financing)
- Non-economic factors (e.g. cultural attitudes towards entrepreneurship, access to education and training, government policies and regulations)
- Demographic factors (e.g. age, gender, education level, social status)
- Industry-specific factors (e.g. market conditions, level of competition, access to resources)
- Regional factors (e.g. availability of infrastructure, level of urbanization, access to markets)
For-profit entrepreneurs are individuals who start businesses with the goal of generating profits for themselves and their stakeholders. These entrepreneurs typically focus on developing products or services that meet the needs of the market and generating revenue through sales.
Not-for-profit entrepreneurs are individuals who start organizations with the goal of achieving a social or environmental mission. These entrepreneurs typically focus on developing innovative solutions to social or environmental problems and generating revenue through grants, donations, or other forms of fundraising.
Constraints for the Growth of Entrepreneurial Culture:
- Lack of access to capital and financing
- Limited availability of infrastructure and support services
- Regulatory and legal barriers
- Cultural and societal attitudes towards entrepreneurship
- Lack of access to education and training
- Limited availability of technology and resources
Entrepreneurship as a Career:
- Entrepreneurship offers individuals the opportunity to pursue their passions and interests while taking on the risks and rewards of starting and running their own businesses.
- Entrepreneurship can provide individuals with greater flexibility and autonomy over their work and personal lives.
- Entrepreneurship can offer the potential for financial rewards and personal fulfillment.
Entrepreneurship as a Style of Management:
- Entrepreneurship as a style of management emphasizes creativity, innovation, and risk-taking as key drivers of organizational success.
- Entrepreneurial managers are focused on identifying and pursuing new business opportunities, developing innovative solutions to problems, and adapting to changing market conditions.
- Entrepreneurial management requires a willingness to take risks, a focus on innovation and creativity, and the ability to think strategically about the organization's goals and objectives.
Emerging Models of Corporate Entrepreneurship:
- Corporate entrepreneurship involves the development of new businesses or ventures within an existing organization.
- Emerging models of corporate entrepreneurship include:
- Incubation and acceleration programs
- Venture capital investments
- Corporate venture capital funds
- Strategic partnerships and collaborations with startups
- Acquisition of startups or innovative technologies
India's Start-Up Revolution – Trends, Imperatives, Benefits:
- India's start-up ecosystem has been rapidly growing in recent years, fueled by government initiatives and increased access to capital and resources.
- Trends in India's start-up ecosystem include:
- Increased focus on technology and innovation
- Greater participation of women and minority entrepreneurs
- Greater collaboration between start-ups and established businesses
- Imperatives for sustaining the growth of India's start-up ecosystem include:
- Addressing infrastructure and regulatory challenges
- Encouraging greater access to capital and resources
- Promoting entrepreneurship education and training
- Benefits of India's start-up revolution include:
- Job creation and economic growth
- Innovation and technological progress
- Increased competitiveness in global markets
Players Involved in India's Start-Up Ecosystem:
- Government agencies and initiatives, such as the Start-Up India program and the Atal Innovation Mission
- Angel investors and venture capital firms
- Business incubators and accelerators
- Educational institutions and entrepreneurship programs
- Established corporations and industry associations
Business Incubators – Rural Entrepreneurship, Social Entrepreneurship, Women Entrepreneurs:
- Business incubators are organizations that provide support and resources to entrepreneurs and start-ups.
- Incubators can be specialized to support different types of entrepreneurs, such as those in rural areas, social entrepreneurs, and women entrepreneurs.
- Rural entrepreneurship incubators may focus on developing businesses that address the unique challenges and opportunities of rural communities.
- Social entrepreneurship incubators may focus on supporting ventures that address social or environmental problems.
- Women entrepreneurship incubators may focus on providing resources and support to women entrepreneurs, who often face unique challenges and barriers to success.
Cases of Tata, Birlas, Kirloskar, and New Generation Entrepreneurs in India:
The Tata Group
- The Tata Group is one of the largest and oldest business conglomerates in India, with interests in industries ranging from steel and automobiles to hospitality and telecommunications.
- The group was founded by Jamsetji Tata in the 19th century and has since been led by several generations of the Tata family.
- Under the leadership of Ratan Tata, the group expanded its global footprint and diversified into new industries such as information technology and aviation.
- The Tata Group is known for its strong commitment to corporate social responsibility, with initiatives such as the Tata Trusts and the Tata Social Welfare and Development Trust.
The Birla Group:
- The Birla Group is another prominent Indian business conglomerate, with interests in industries such as cement, textiles, and chemicals.
- The group was founded by Ghanshyam Das Birla in the early 20th century and has since been led by several generations of the Birla family.
- The group is known for its philanthropic initiatives, such as the Birla Institute of Technology and Science and the Birla Planetarium.
New Generation Entrepreneurs in India:
- In recent years, India has seen the rise of a new generation of entrepreneurs who are building innovative and disruptive businesses across a variety of industries.
- Examples of new generation entrepreneurs in India include:
- Bhavish Aggarwal, founder of ride-hailing service Ola
- Sachin Bansal and Binny Bansal, founders of e-commerce platform Flipkart
- Vijay Shekhar Sharma, founder of digital payments company Paytm
- Ritesh Agarwal, founder of budget hotel chain OYO
These entrepreneurs are known for their innovative ideas, ability to disrupt traditional industries, and willingness to take on risk and uncertainty in pursuit of their goals.
Chapter 2: Theories of entrepreneurship
Innovation Theory by Schumpeter:
- Joseph Schumpeter's Innovation Theory posits that entrepreneurs drive economic growth and development by introducing new products, services, and production methods.
- According to Schumpeter, innovation is the primary force that disrupts existing markets and creates new ones.
- Schumpeter identified five types of innovation: the introduction of new products, the introduction of new production methods, the opening of new markets, the acquisition of new sources of supply, and the establishment of new industry structures.
Theory of High Achievement by McClelland:
- David McClelland's Theory of High Achievement proposes that individuals with a strong need for achievement are more likely to become successful entrepreneurs.
- According to McClelland, high achievers are characterized by their desire for personal responsibility, feedback, and challenging goals.
- McClelland suggested that entrepreneurial success can be fostered through training and development programs that emphasize goal-setting, risk-taking, and performance feedback.
X-Efficiency Theory by Leibenstein:
- Harvey Leibenstein's X-Efficiency Theory argues that firms can operate at different levels of efficiency, and that the level of efficiency is influenced by the management's commitment to minimizing waste and maximizing productivity.
- According to Leibenstein, firms that operate at a high level of efficiency can achieve higher profits and gain a competitive advantage in the market.
- Leibenstein suggested that factors such as bureaucracy, lack of motivation, and information asymmetry can lead to a reduction in a firm's efficiency.
Theory of Profit by Knight:
- Frank Knight's Theory of Profit posits that profits are a reward for entrepreneurial risk-taking and uncertainty-bearing.
- According to Knight, entrepreneurs are unique in their willingness to take on uncertainty and the potential for loss, and they are rewarded with profits when their investments succeed.
- Knight argued that the potential for profit is necessary to incentivize entrepreneurs to take risks and innovate.
Theory of Social Change by Everett Hagen:
- Everett Hagen's Theory of Social Change posits that changes in a society's economic and social structure can lead to changes in the values, beliefs, and attitudes of individuals.
- According to Hagen, entrepreneurs play a critical role in driving social change by introducing new products, services, and business models that challenge the status quo.
- Hagen suggested that social change occurs when entrepreneurs succeed in convincing individuals to adopt new values and behaviors that are aligned with their innovations.
Chapter 3: Entrepreneurship development
Entrepreneurial competencies refer to the skills, knowledge, and attitudes required for successful entrepreneurship.
- Some key entrepreneurial competencies include opportunity identification, risk-taking, creativity and innovation, networking, resource management, and leadership.
Developing Competencies
- Developing entrepreneurial competencies involves identifying the areas in which an entrepreneur needs to improve and providing opportunities for learning and skill development.
- Competency development can occur through a variety of means, including formal training programs, mentoring and coaching, and experiential learning opportunities.
Concept of Entrepreneurship Development
- Entrepreneurship development refers to the process of creating an environment that fosters and supports entrepreneurship.
- The goal of entrepreneurship development is to increase the number and success rate of entrepreneurs by providing access to resources, training, and other forms of support.
Entrepreneur Training and Developing
- Entrepreneur training and development programs provide entrepreneurs with the knowledge, skills, and attitudes required for successful entrepreneurship.
- These programs can include formal training courses, workshops, mentoring and coaching, and experiential learning opportunities.
Role of Entrepreneur Development Programs (EDP):
- Entrepreneur Development Programs (EDP) play a critical role in fostering entrepreneurship by providing entrepreneurs with access to training, resources, and other forms of support.
- EDPs can be run by government agencies, non-profits, universities, and other organizations.
EDP - Objectives – contents – methods - execution:
- The objectives of an Entrepreneur Development Program (EDP) are to equip entrepreneurs with the knowledge, skills, and attitudes required for successful entrepreneurship and to facilitate the creation and growth of new businesses.
- The contents of an EDP can include topics such as business planning, market research, financial management, and legal issues.
- Methods for delivering an EDP can include classroom instruction, mentorship, and experiential learning opportunities such as internships or business incubation programs.
- Execution of an EDP can involve collaboration between government agencies, non-profits, universities, and other organizations, and can include both in-person and online training programs.
Role of DIC, SISI, EDII, NIESBUD, NEDB
- Development Commissioner (DIC): DICs are responsible for promoting, developing and facilitating the growth of small-scale industries in India. They provide assistance to entrepreneurs in setting up their businesses by providing information on government schemes, policies, and incentives, as well as support services like training, marketing, and finance.
- Small Industries Service Institute (SISI): SISIs are technical training institutes that provide training, research, and consultancy services to small-scale industries. They offer a range of services like product design, quality control, testing, packaging, and marketing, as well as training programs for entrepreneurs and their employees.
- Entrepreneurship Development Institute of India (EDII): EDII is an autonomous institute that offers training, research, and consultancy services to entrepreneurs, aspiring entrepreneurs, and other stakeholders in the entrepreneurship ecosystem. They provide various services like business incubation, mentoring, and coaching, as well as customized training programs for different sectors and target groups.
- National Institute for Entrepreneurship and Small Business Development (NIESBUD): NIESBUD is an apex institute for entrepreneurship and small business development in India. It offers various training programs, research, and consultancy services to entrepreneurs, as well as support for business incubation and technology transfer. NIESBUD also provides accreditation and certification for various entrepreneurship-related courses and programs.
- National Entrepreneurship Development Board (NEDB): NEDB is a central government agency responsible for promoting entrepreneurship and small business development in India. It offers a range of services to entrepreneurs like business incubation, mentorship, training, and access to finance. NEDB also coordinates with other government agencies, financial institutions, and industry associations to create a conducive ecosystem for entrepreneurship in India.
Role of Mentors:
- Mentors play a critical role in the success of entrepreneurs by offering guidance, support, and feedback.
- Mentors can provide valuable insights and advice on business strategies and ideas.
- They can offer encouragement and motivation during difficult times and serve as a sounding board for entrepreneurs.
- Mentors can also help entrepreneurs develop new skills and knowledge and provide valuable networking opportunities.
Innovation and Entrepreneurship, Design Thinking Process:
- Innovation is a key aspect of entrepreneurship, and entrepreneurs need to be creative and innovative to succeed.
- Design thinking is a problem-solving process that can help entrepreneurs develop innovative solutions to problems.
- The design thinking process involves empathy, defining the problem, ideation, prototyping, and testing.
- By following this process, entrepreneurs can develop products and services that meet the needs of their customers and stand out in the marketplace.
Role of consultancy organizations in promoting Entrepreneurs:
- Consultancy organizations can play an important role in promoting entrepreneurship by providing support, advice, and resources to entrepreneurs.
- They can offer assistance with business planning, marketing, and financial management. Consultancy organizations can also provide networking opportunities and help entrepreneurs connect with potential investors and customers.
- By providing these services, consultancy organizations can help entrepreneurs overcome the challenges of starting and growing a business.
Problems and difficulties of Entrepreneurs:
- Entrepreneurs face many challenges when starting and growing a business, including marketing, finance, human resource, and production challenges.
- Marketing challenges include developing effective marketing strategies, identifying target customers, and building brand awareness.
- Finance challenges include securing funding, managing cash flow, and forecasting financial performance.
Difficulties of Entrepreneurs:
- Marketing:
- Finding and reaching target customers
- Establishing a brand identity and differentiating from competitors
- Developing effective marketing strategies within budget constraints
- Finance:
- Raising capital to start or expand the business
- Managing cash flow and budgeting
- Understanding and complying with tax regulations and financial reporting requirements
- Human Resources:
- Recruiting and retaining talented employees
- Managing and motivating employees
- Complying with employment laws and regulations
- Production:
- Managing inventory and supply chain logistics
- Ensuring quality control and product consistency
- Optimizing production processes for efficiency and cost-effectiveness
Research:
- External Problems:
- Economic conditions, such as recessions or inflation
- Changes in consumer preferences and market trends
- Competitor actions, such as pricing or marketing strategies
- Mobility of Entrepreneurs:
- Access to resources and infrastructure, such as funding, networks, and technology
- Regional or national policies that encourage or discourage entrepreneurship
- Personal factors, such as education, experience, and risk tolerance
- Entrepreneurial Change:
- Adapting to new technologies, markets, or regulations
- Responding to customer feedback and changing demands
- Implementing new business models or strategies
- Occupational Mobility:
- Availability of job opportunities and career paths
- Transferability of skills and experience across different industries or sectors
- Personal motivations and goals, such as work-life balance or social impact
Chapter 4: Role of Government promoting Entrepreneurship
Introduction to various incentives, subsidies and grants:
- Incentives, subsidies, and grants are financial assistance provided by the government or other organizations to encourage or support certain activities, such as business investment, research and development, or environmental sustainability.
- Some common types of incentives, subsidies, and grants include tax breaks, low-interest loans, cash grants, and in-kind support (such as free or reduced-cost training or equipment).
Export Oriented Units:
- Export-oriented units (EOUs) are business entities that specialize in exporting goods or services to other countries.
- EOUs may receive various benefits, such as tax breaks, duty-free imports of raw materials and machinery, and streamlined customs procedures.
- EOUs are often located in special economic zones or free trade zones, which offer additional incentives and regulatory flexibility.
Fiscal and Tax concessions available:
- Fiscal and tax concessions refer to policies that reduce or eliminate tax obligations for certain businesses or activities.
- These concessions may include tax credits, deductions, exemptions, or deferrals.
- Some common types of fiscal and tax concessions include research and development tax credits, investment tax credits, and accelerated depreciation schedules.
Women Entrepreneurs - Role, Problems and Prospects:
- Women entrepreneurs are women who own and operate their own businesses.
- Women entrepreneurs play an important role in the economy by creating jobs, driving innovation, and contributing to economic growth.
- Women entrepreneurs face unique challenges and barriers, such as gender discrimination, lack of access to capital and resources, and societal expectations around gender roles.
- Despite these challenges, the prospects for women entrepreneurs are improving, with increased support from governments, investors, and business networks.
Reasons for low women Entrepreneurs:
- There are several reasons why women may be underrepresented in entrepreneurship, including social and cultural norms, lack of access to resources and funding, and discrimination and bias.
- Women may also face additional barriers related to family responsibilities and work-life balance.
- Addressing these barriers and increasing support for women entrepreneurs can help to create a more inclusive and diverse entrepreneurial ecosystem.
Assistance Programme for Small Scale Units:
- Assistance programs for small scale units (SSUs) are initiatives undertaken by the government or other organizations to support the growth and development of small businesses.
- These programs may include financial assistance, such as loans or grants, as well as non-financial assistance, such as training, marketing support, and access to resources and networks.
Institutional Framework:
- The institutional framework for SSUs refers to the policies, regulations, and organizations involved in supporting the growth and development of small businesses.
- This framework may include government agencies, financial institutions, trade associations, and other organizations that provide assistance and support to SSUs.
Role of SSI Sector in the Economy:
- The small scale industry (SSI) sector plays an important role in the economy by creating jobs, promoting innovation, and supporting local communities.
- SSIs are often involved in producing goods and services for local markets, which can contribute to economic development and stability.
- SSIs may also be more flexible and responsive to changing market conditions, making them important contributors to economic growth.
SSI Units – Failure, Causes and Preventive Measures:
- SSI units may fail for a variety of reasons, such as poor management, lack of access to capital, and changing market conditions.
- Preventive measures may include improving management and financial skills, developing new products or services, and accessing new markets.
- Other strategies may include building partnerships with other businesses or organizations, or seeking assistance from government or other support networks.
Turnaround Strategies:
- Turnaround strategies are plans and actions taken to help a struggling business overcome its challenges and become profitable again.
- These strategies may include restructuring the business, reducing costs, improving efficiency, and developing new products or markets.
- Other strategies may include seeking new investors or partners, or developing a new business model that better aligns with changing market conditions.
Future of Entrepreneurship Development and Government:
- The future of entrepreneurship development and government is likely to be shaped by increasing digitalization, globalization, and changing societal attitudes toward entrepreneurship.
- Governments are likely to play an important role in supporting entrepreneurship through policies and programs that promote innovation, access to resources and networks, and opportunities for growth and development.
- Other trends may include increasing focus on sustainability and social entrepreneurship, as well as greater participation by women and other underrepresented groups in entrepreneurship.
Start Up India:
- Start Up India is an initiative launched by the Indian government in 2016 to support the growth and development of startup businesses.
- The initiative includes a range of programs and policies designed to promote entrepreneurship, including financial incentives, regulatory reforms, and access to resources and networks.
- Start Up India aims to create a more supportive environment for startups, with the goal of promoting innovation, job creation, and economic growth.
Make in India:
- Make in India is an initiative launched by the Indian government in 2014 to promote manufacturing and investment in India.
- The initiative aims to encourage businesses to invest in India by providing a more favorable business environment, including streamlined regulations, improved infrastructure, and access to resources and networks.
- Make in India aims to promote economic growth and development by boosting manufacturing, creating jobs, and attracting investment to India.
Chapter 5: Enterprise Promotion
Creating Entrepreneurial Venture:
- Creating an entrepreneurial venture involves identifying a market opportunity, developing a viable business idea, and creating a plan to bring the idea to market.
- Successful entrepreneurial ventures require a combination of creativity, innovation, and business acumen.
Entrepreneurship Development Cycle:
- The entrepreneurship development cycle involves several stages, including idea generation, opportunity assessment, business planning, resource acquisition, and launch and growth of the venture.
- Each stage of the cycle requires specific skills and knowledge, and successful entrepreneurs must be able to navigate each stage effectively.
Business Planning Process:
- The business planning process involves developing a comprehensive plan for bringing an entrepreneurial idea to market.
- This process typically involves conducting market research, identifying resources and capabilities needed to develop the idea, creating financial projections, and developing a marketing strategy.
The business plan as an entrepreneurial tool:
- The business plan is an important tool for entrepreneurs, as it provides a roadmap for bringing an entrepreneurial idea to market.
- A well-developed business plan can help entrepreneurs identify potential challenges and opportunities, and can provide guidance for decision-making and resource allocation.
Elements of Business Plan:
- The elements of a business plan typically include an executive summary, company description, market analysis, product or service description, marketing and sales strategy, management and organizational structure, financial projections, and funding requirements.
Objectives:
- Objectives are goals that an entrepreneur hopes to achieve through their entrepreneurial venture.
- Objectives may include financial goals, such as revenue or profit targets, as well as non-financial goals, such as social or environmental impact.
Market Analysis:
- Market analysis is an important component of the business planning process, as it involves identifying target markets, analyzing competitors, and understanding customer needs and preferences.
- Market analysis helps entrepreneurs develop effective marketing strategies and positioning, and can provide valuable insights into the viability of a business idea.
Identifying attributes of strategic resources:
- Strategic resources are resources that are critical to the success of a business, and which are difficult for competitors to replicate.
- Attributes of strategic resources may include factors such as uniqueness, rarity, inimitability, and non-substitutability.
Opportunity Analysis:
- Opportunity analysis involves identifying and evaluating potential market opportunities for an entrepreneurial venture.
- This process typically involves analyzing customer needs and preferences, assessing market size and growth potential, and evaluating potential competition and barriers to entry.
Innovator or imitator:
- Entrepreneurs may choose to be innovators or imitators in their respective markets.
- Innovators develop new and unique products or services, while imitators seek to replicate existing products or services in a more efficient or cost-effective manner.
SWOT analysis:
- SWOT analysis is a strategic planning tool that helps entrepreneurs assess their internal strengths and weaknesses, as well as external opportunities and threats.
- This analysis can help entrepreneurs develop strategies to capitalize on their strengths and opportunities, while mitigating their weaknesses and threats.
Internal and External Environment Analysis:
- Internal and external environment analysis involves evaluating the internal strengths and weaknesses of a business, as well as external opportunities and threats.
- This analysis can help entrepreneurs develop strategies to capitalize on their strengths and opportunities, while mitigating their weaknesses and threats.
Industry Analysis:
- Industry analysis involves evaluating the competitive dynamics of a particular industry or market.
- This analysis can help entrepreneurs identify key competitors, understand market trends and growth potential, and develop strategies to compete effectively.
Embryonic Companies and Spinoffs:
- Embryonic companies are newly-formed ventures that are still in the early stages of development.
- Spinoffs are new ventures that are created from an existing company, typically with the goal of leveraging existing resources and capabilities.
Porter's Five Forces Model:
- Porter's Five Forces Model is a framework for analyzing the competitive dynamics of a particular industry or market.
- The model considers factors such as the bargaining power of suppliers, the bargaining power of buyers, the threat of new entrants, the threat of substitutes, and the intensity of competitive rivalry.
Identifying the right Business Model Canvas:
- The Business Model Canvas is a strategic planning tool that helps entrepreneurs develop and refine their business models.
- To identify the right Business Model Canvas, entrepreneurs must consider factors such as customer needs and preferences, market size and growth potential, competitive dynamics, and resource requirements.
Seven Domains of John Mullins:
- The Seven Domains of John Mullins is a framework for evaluating the viability of a business idea.
- The framework considers factors such as market attractiveness, industry structure, competitive dynamics, resource requirements, founder experience and capabilities, financial projections, and exit strategy.
Opportunities in Emerging/Transition/Decline industries:
- Emerging industries are those that are just beginning to gain traction, while transition industries are those that are experiencing significant changes in technology, consumer preferences, or other factors.
- Decline industries are those that are experiencing a decline in demand or market share.
- Opportunities in these industries may include developing new products or services that address emerging or changing consumer needs, or finding ways to revitalize existing businesses through innovation or cost-cutting measures.
Opportunities at the Bottom of the Pyramid:
- The bottom of the pyramid refers to the billions of people around the world who live on less than $2 per day.
- Opportunities in this market may include developing affordable products or services that meet the needs of this population, or finding ways to empower individuals and communities through entrepreneurship and job creation.
Opportunities in Social Sector:
- The social sector refers to organizations and businesses that are focused on addressing social or environmental issues.
- Opportunities in this sector may include developing innovative solutions to social and environmental challenges, or finding ways to create sustainable business models that also have a positive impact on society.
Opportunities arising out of digitization:
- Digitization refers to the transformation of analog information into digital form.
- Opportunities in this area may include developing digital products or services that leverage new technologies such as artificial intelligence, blockchain, or virtual and augmented reality, or finding ways to leverage digital platforms and channels to reach new customers or markets.
Marketing:
- Marketing involves identifying customer needs and preferences, developing products or services that meet those needs, and promoting those products or services to the target market.
- Effective marketing strategies may include developing a strong brand identity, leveraging digital marketing channels, and conducting market research to identify customer needs and preferences.
Finance:
- Finance involves managing the financial resources of a business, including budgeting, forecasting, and financial reporting.
- Effective finance strategies may include developing a strong financial plan, managing cash flow effectively, and seeking out funding sources such as loans, grants, or equity investments.
Organization & Management:
- Organization and management involve developing effective systems and processes for managing employees and operations.
- Effective organization and management strategies may include developing a strong company culture, implementing effective performance management systems, and building effective teams.
Ownership - Franchising, networking and alliances, Buying an existing business:
- Different ownership models may be appropriate for different types of businesses.
- Franchising may be a good option for businesses that want to leverage an established brand and business model.
- Networking and alliances may be a good option for businesses that want to collaborate with other businesses in the same industry or market.
- Buying an existing business may be a good option for entrepreneurs who want to reduce risk by acquiring an established customer base and operating history.
Critical risk contingencies of the proposal:
- Developing a successful business plan requires careful consideration of potential risks and contingencies.
- Critical risk contingencies may include factors such as changes in market demand or competitive dynamics, changes in regulations or laws, or unexpected events such as natural disasters or economic downturns.
Scheduling and Milestones:
- Scheduling and milestones are critical for ensuring that a business plan is executed effectively.
- Scheduling may involve developing a timeline for product development, marketing and sales activities, and other key milestones.
- Milestones may include achieving specific revenue or profitability targets, launching a new product or service, or achieving other key business objectives.

.jpeg)