A balance sheet is a financial statement that shows a company's assets, liabilities, and equity at a particular point in time. The balance sheet is divided into two sections, the assets section, and the liabilities and equity section. Here are some of the particulars you may find in each section of a balance sheet:
Assets:
Current assets: These are assets that are expected to be converted into cash within one year. Examples include cash, accounts receivable, inventory, and prepaid expenses.
Property, plant, and equipment: These are long-term assets that are used in the production of goods or services. Examples include buildings, machinery, and vehicles.
Intangible assets: These are assets that do not have a physical form but have value, such as patents, trademarks, and copyrights.
Liabilities and Equity:
Current liabilities: These are debts that are due within one year. Examples include accounts payable, short-term loans, and accrued expenses.
Long-term liabilities: These are debts that are due over a period of more than one year. Examples include mortgages, long-term loans, and bonds.
Equity: This represents the owner's claim to the assets of the company after all liabilities have been paid. It includes common stock, preferred stock, retained earnings, and other equity accounts.
A profit and loss (P&L) statement, also known as an income statement, is a financial statement that summarizes a company's revenue and expenses over a specified period of time. The primary goal of a P&L statement is to calculate the company's net income or loss. Here are some of the particulars you may find in a P&L statement:
- Revenue: This is the total amount of money a company earns from its business operations during the specified period. Revenue may be broken down into various categories such as sales revenue, service revenue, and rental revenue.
- Cost of Goods Sold (COGS): This is the direct cost incurred by a company in producing its goods or services. Examples include raw materials, direct labor, and production overheads.
- Gross profit: This is the revenue minus the COGS, and it represents the profit made before deducting other expenses.
- Operating expenses: These are the expenses incurred in running a business that are not directly related to producing the goods or services. Examples include salaries, rent, utilities, advertising, and depreciation.
- Operating income: This is the gross profit minus the operating expenses and represents the profit made from the core operations of the business.
- Other income and expenses: This includes any income or expenses that are not related to the core operations of the business. Examples include interest income, interest expense, and gains or losses from the sale of assets.
- Net income: This is the total profit or loss made by the company during the specified period, calculated by subtracting all expenses from the revenue.
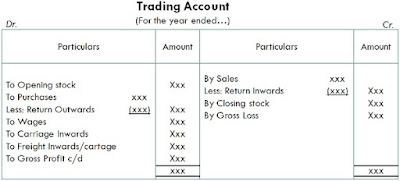
- Opening stock: This is the value of stock held by the company at the beginning of the period.
- Purchases: This is the total value of all goods purchased during the period.
- Direct expenses: These are expenses that are directly related to the purchase of goods, such as transportation costs and customs duty.
- Closing stock: This is the value of stock held by the company at the end of the period.
- Sales: This is the total value of all goods sold during the period.
- Gross profit: This is the difference between the sales and the cost of goods sold (opening stock + purchases - closing stock), and it represents the profit made from trading operations.
- Indirect expenses: These are expenses that are not directly related to the purchase or sale of goods, such as rent, salaries, and utilities.
- Net profit: This is the gross profit minus the indirect expenses and represents the total profit made by the company from its trading operations.

.jpeg)